Project management 3. GitHub tools
Issues
- Issues: tasks that need to be done
- Creating a new issue
- You can add a description
- You can set an assignee to an issue
- You can tag issue with a label
- Feature, bug, code
- level design, story…
- You can also link issue to a project
- When issue is done, you close it with Close issue
- Note: You can auto-close an issue with a commit message
"fix #<issuenumber>" or "close #<issuenumber>"
- Note: You can add todo lists into the description!
- Todo list can include links to other issues (just write #issuenumber)
- Don’t create a mega-issue “Sprint 1” or something like that, however
- We have a better tool for that…
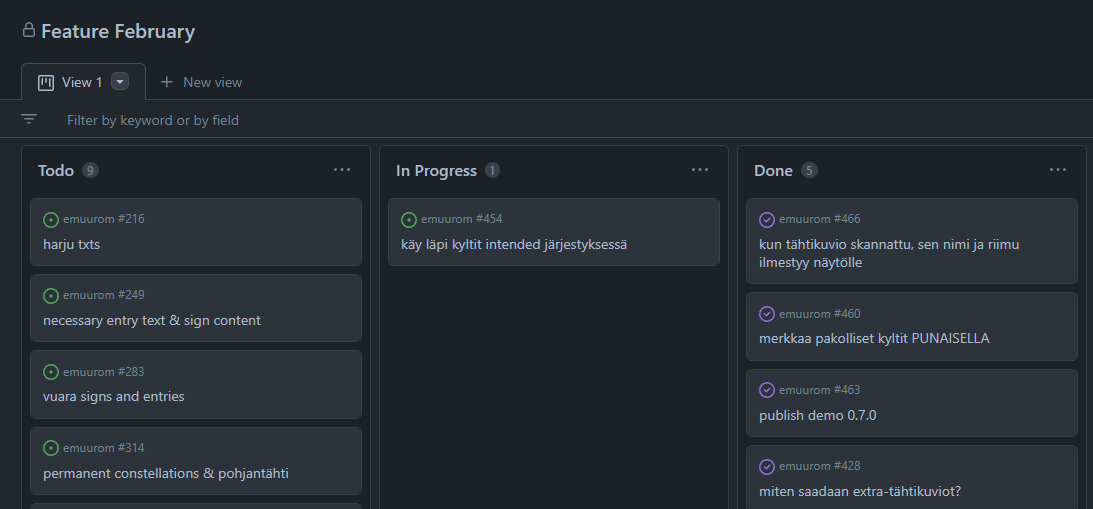
Projects
- A board that can be used to track sprint progress
- GitHub has two Projects views
- Projects
- Projects (Beta)
- Can have issues from multiple repos
- Create a new project (not beta) for every sprint under Projects Tab > Projects (not beta!) > New Project
- Give name “Sprint 1”
- Use Project template “Automated kanban”
- Delete the default notes
- Now, when an issue is closed, it jumps automatically to Done column
- Kanban board has by default three columns of issues & notes
- There can be issues, pull requests and notes in the columns
- Notes can be converted into issues
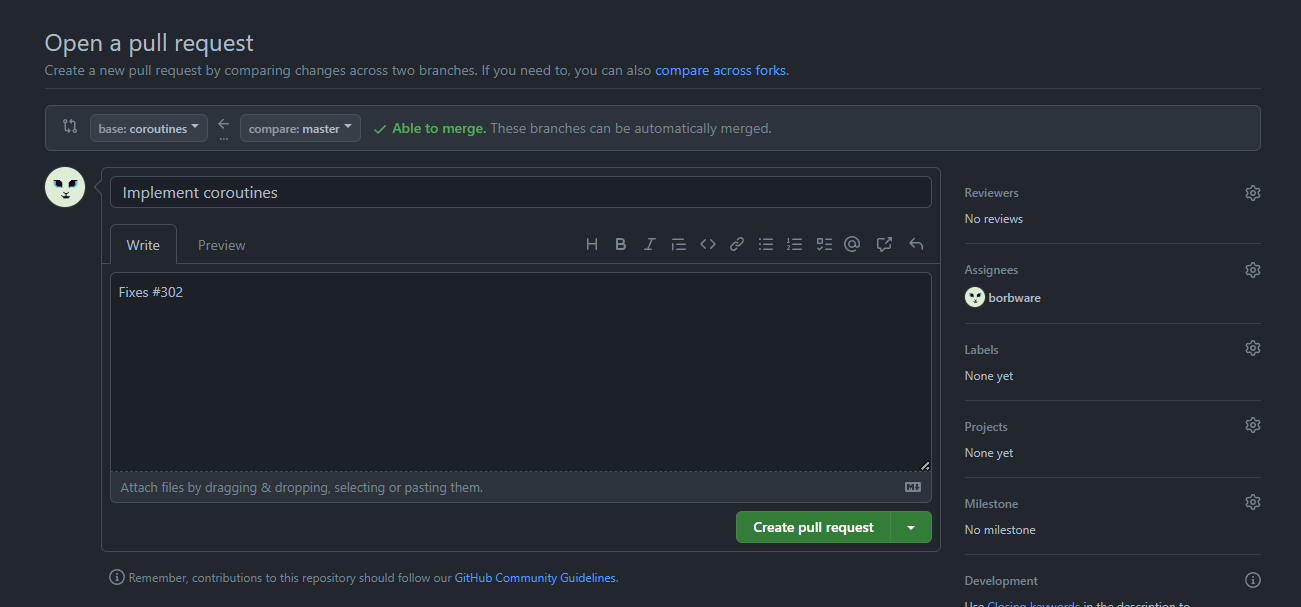
Pull requests
- The recommended way to merge a feature branch into the master branch
- When a branch is ready to be merged into master, create a pull request in this tab
- If the master branch maintainer doesn’t accept it right away, they can comment on the pull request page what needs to be changed before merge can be completed
- If “All comments need to be resolved” is checked, the merge can only be completed after you’ve addressed the issues and the maintainer has approved the changes!
- After making these changes, you don’t have to create a new pull request, new commits are automatically added to the one already created
Searching for specific issues and pull requests
- You can search for issues or pull requests with specific dates, etc.
- The syntax is versatile, check these links for more info:

